

Therefore, we observe an increased population and diversity of plant and animal species here.
However, we’re talking about ecotones here, which implies that there are two ecosystems to be considered.Īs mentioned above, an ecotone represents the transition region between two ecosystems. In our context, the “edge effect” relates to the outer limit of a particular ecosystem. The literal meaning of the term “edge” is the outside limit of a surface or an area. Similarly, when one talks about ecotones, discussing the “edge effect” is unavoidable. When we talk about global diplomacy, we inevitably quote Machiavelli. Therefore, the variation produced in such areas contributes to increased biodiversity! What is the edge effect?

Such species are often not found in the adjacent ecosystems. Moreover, in ecotones, certain other species that are specially adapted for living in this zone will also thrive. This is because they contain animal and plant species from both the adjacent ecosystems. The transitioning region boasts species richness and elaborate biodiversity. Not only this, but ecotones are also very special when it comes to species diversity. Several amphibians thrive in ecotones (Photo Credit : Jay Ondreicka/Shutterstock) Apart from this, marshes, mangroves, and coastal ecosystems are great examples of ecotonal regions. This is why ecotones are very common in mountain ranges because of the wide variety of climatic conditions observed on the slopes. These regions form due to a variety of different factors, such as climate, location, temperature, etc. This means that there is a delicate zone where the blending of flora and fauna occurs. However, there are no sharp boundaries between most ecosystems. For instance, if we were to consider the ocean as our area, then the ecosystem in question would be referred to as the marine ecosystem. The living components include plants and animals, while the non-living components include the soil, weather, sunlight, water, etc. An ecosystem is an area where all living components interact with the non-living components to maintain their small bubble of life.
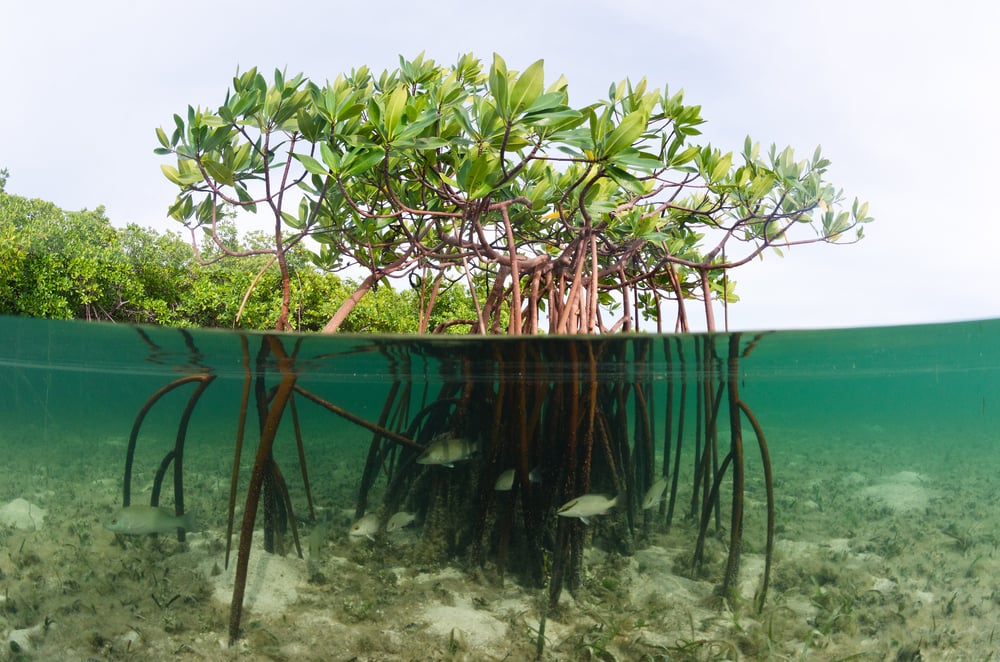

How is an ecotone formed?īefore diving into this question, we must first understand what an ecosystem is. A marshland exists between a river and a riverbank, meaning that it is different than either of the two bordering ecosystems in terms of its biological characteristics. In order to understand this term clearly, you can consider the example of marshy land. One may also consider this place as a transition zone, since it’s different than either of the two ecosystems that it lies between. And start practicing bisociation towards new patterns of things to come.An ecotone is an area that represents the boundary between two ecosystems. Awaken your eagle eyes so that surprises can be transformed into something valuable. So, if you wake up tomorrow and if you decide to do some edge work, make sure that you position yourself in the flow and become a co-worker with the creative force of evolution. In my experience, this means dancing between the rational concrete mind and the intuitive abstract mind so that new matrixes of meaning can emerge. For this to happen edge workers tend to move from thinking on a single ‘plane’ to the creative act of thinking on multiple planes. In bisociation, you basically bring together two ideas or things that seem to have nothing in common and see what results you get. Proposed by Koestler in his book The Act of Creation, bisociation can be described as a “spontaneous flash of insight.which connects previously unconnected matrices of experience”, in other words, the Aha moment! The concept of bisociation involves connecting two seemingly unrelated things into a new matrix of meaning.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
